Tableau constituye una plataforma de inteligencia de negocios enfocada en la transformación de datos complejos en visualizaciones interactivas y dashboards intuitivos.
La herramienta facilita la conexión a múltiples orígenes de información, el análisis interactivo y la comunicación de insights estratégicos, permitiendo a usuarios de distintos niveles extraer valor en tiempo real sin depender exclusivamente de procesos tradicionales.
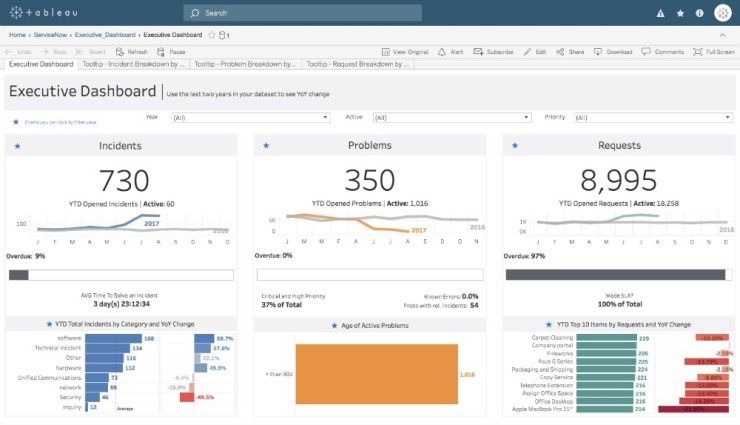
Tableau es una de las herramientas líderes en business intelligence, transformando datos complejos en visualizaciones impactantes y dashboards interactivos que facilitan la toma de decisiones estratégicas.
La aplicación destaca por su capacidad de integrar orígenes heterogéneos —desde bases de datos relacionales hasta servicios en la nube— mediante una arquitectura modular que maximiza la eficiencia en la manipulación de volúmenes significativos de datos. La experiencia del usuario se ve realzada gracias a su interfaz intuitiva, en la que el método de arrastrar y soltar propicia la elaboración de informes personalizados, dotados de funcionalidades como el filtrado dinámico y el drill down, elementos clave para el descubrimiento de insights estratégicos.
Mediante avanzadas capacidades de preparación y transformación, Tableau impulsa la integración de datos en tiempo real, permitiendo que los equipos de análisis generen soluciones colaborativas a través de plataformas como Tableau Server y Tableau Online. La herramienta ofrece, además, soporte para la incorporación de cálculos complejos y la interconexión con lenguajes programáticos, lo cual amplía las posibilidades dentro de entornos empresariales exigentes.
Desde el punto de vista técnico, la robusta infraestructura de Tableau optimiza el rendimiento en consultas y procesamiento de grandes cantidades de información, lo que se traduce en buenos tiempos de respuesta y una alta interactividad en la exploración de datos. Su extensa comunidad de usuarios y los recursos formativos disponibles contribuyen a una continua evolución de la plataforma, adaptándose a las necesidades cambiantes del análisis empresarial.
Componentes principales de Tableau
-
Tableau Desktop: Es el entorno principal para conectar, limpiar y modelar datos. Su interfaz de arrastrar y soltar habilita la creación de visualizaciones y dashboards altamente personalizables sin requerir conocimientos avanzados de programación. Además, permite definir cálculos complejos mediante expresiones y utilizar herramientas analíticas integradas para descubrir tendencias y patrones.
-
Tableau Server y Tableau Online: Estas soluciones ofrecen la publicación, compartición y colaboración en torno a dashboards e informes interactivos. Gracias a ellas, las visualizaciones pueden distribuirse de forma segura dentro de la organización, actualizándose automáticamente y posibilitando la interacción en tiempo real entre equipos de diferentes áreas.
-
Tableau Prep: Se encarga de la preparación y transformación de datos, facilitando la limpieza, combinación y estructuración de fuentes heterogéneas, lo que optimiza la calidad de la información desde la etapa inicial del análisis.
-
Tableau Public: Permite crear y compartir visualizaciones en una plataforma gratuita, lo que resulta especialmente útil para la difusión de insights en foros o redes sociales, aunque con ciertas limitaciones de privacidad.
Licenciamiento
-
Tableau Desktop: Disponible bajo modalidad de suscripción (con ediciones Personal y Profesional) con licencia por usuario.
-
Tableau Server: Modalidad empresarial, con opción de instalaciones on-premise y licenciamiento basado en suscripción anual o, en algunos casos, modelos perpetuos.
-
Tableau Online: Servicio en la nube con modelo de suscripción, enfocado en la escalabilidad y colaboración sin infraestructura local.
Tamaño de Empresa
Tableau se adapta a pequeñas, medianas y grandes organizaciones, aunque su implementación resulta especialmente ventajosa en entornos de medianas a grandes empresas donde se manejan volúmenes importantes de información.
Tipo de Instalación
-
On-Premise: Tableau Desktop y Tableau Server permiten la instalación local, ofreciendo control total sobre la infraestructura y la seguridad interna.
-
En la Nube: Tableau Online y Tableau Public brindan soluciones hospedadas que facilitan la escalabilidad y el acceso remoto, ideales para organizaciones que prefieren minimizar la inversión en hardware.
Fortalezas y Debilidades
| Fortalezas | Debilidades |
|---|---|
| - Alta conectividad a múltiples orígenes de datos. | - Curva de aprendizaje pronunciada para aprovechar al máximo sus funcionalidades avanzadas. |
| - Visualizaciones interactivas y personalizables que facilitan el análisis visual. | - Coste elevado en comparación con otras soluciones de BI, lo que puede limitar su adopción en pequeñas empresas. |
| - Potentes capacidades de análisis y preparación de datos que permiten insights en tiempo real. | - Requiere de una infraestructura tecnológica adecuada para el manejo óptimo de grandes volúmenes de información. |
| - Amplia comunidad y recursos formativos que favorecen la actualización y el soporte. | - Limitaciones en la personalización avanzada sin invertir en formación especializada o soporte técnico adicional. |
Recursos sobre Tableau
Curso para aprender a trabajar con Tableau
- Printer-friendly version
- Log in to post comments


